26 Nov 2024
Harnessing SMA technology to solve the VAC challenges of XR
By Nick Heijne, Head of AR/VR
The increasing popularity of Extended Reality (XR) devices has brought the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict (VAC) into focus as a notable challenge needing resolution. VAC is a mismatch between the eye's focus and depth perception in virtual environments that can lead to user discomfort, fatigue, and nausea. Addressing VAC requires innovative solutions, and Cambridge Mechatronics Ltd. (CML) is contributing to this effort with its advanced Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuator technology. By leveraging SMA’s precision, high force, compact size, and power efficiency, CML is developing our technology to enable dynamic focal adjustment in XR headsets, to tackle the VAC challenge.
The VAC challenge in XR
In natural vision, the eyes rely on several cues to perceive depth, among these are: 1) vergence, where the eyes rotate to align on an object, and 2) accommodation, where the lens changes shape to focus. These 2 cues are naturally synchronized, ensuring clear, comfortable vision. In XR environments, however, fixed focal planes disrupt this alignment. While the vergence angle adjusts to track virtual objects, the lack of accommodation adjustment creates a conflict, leading to visual discomfort.
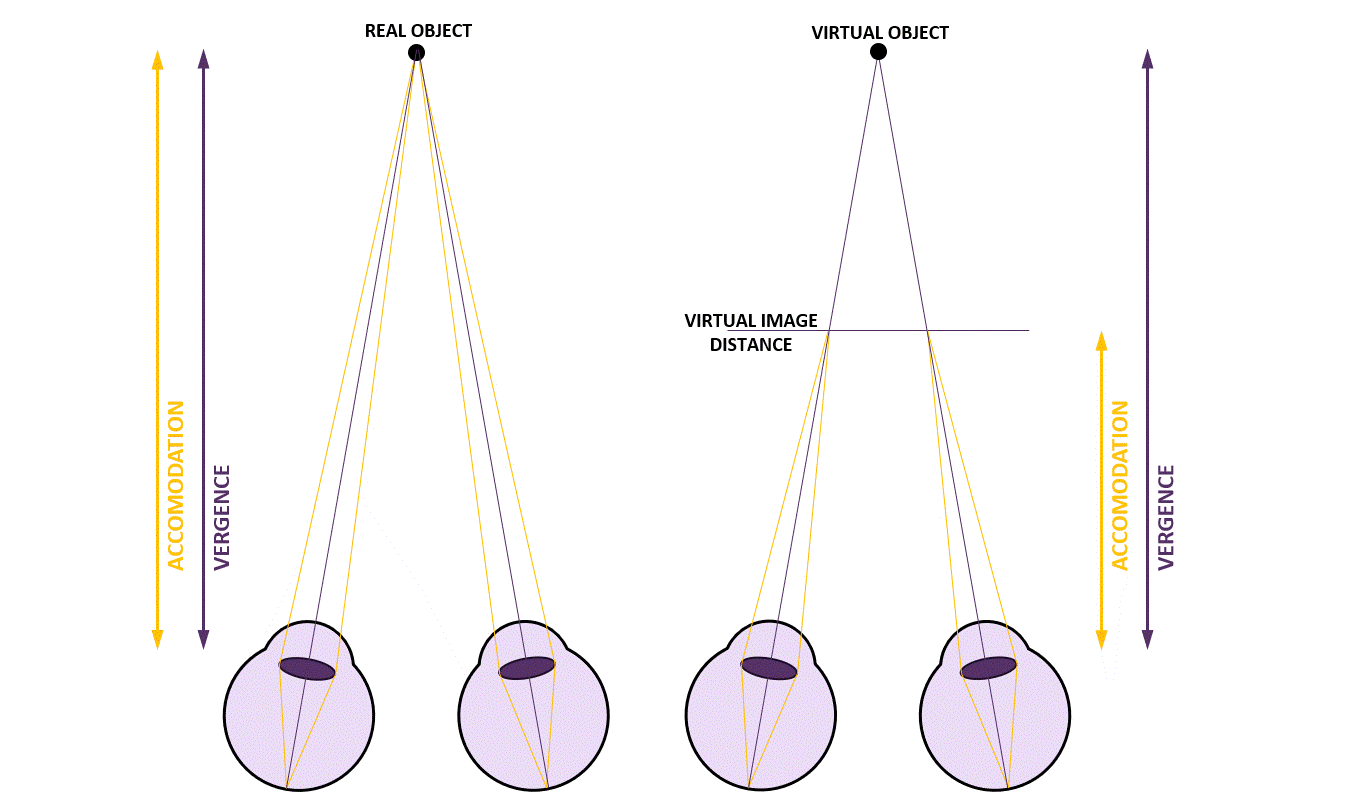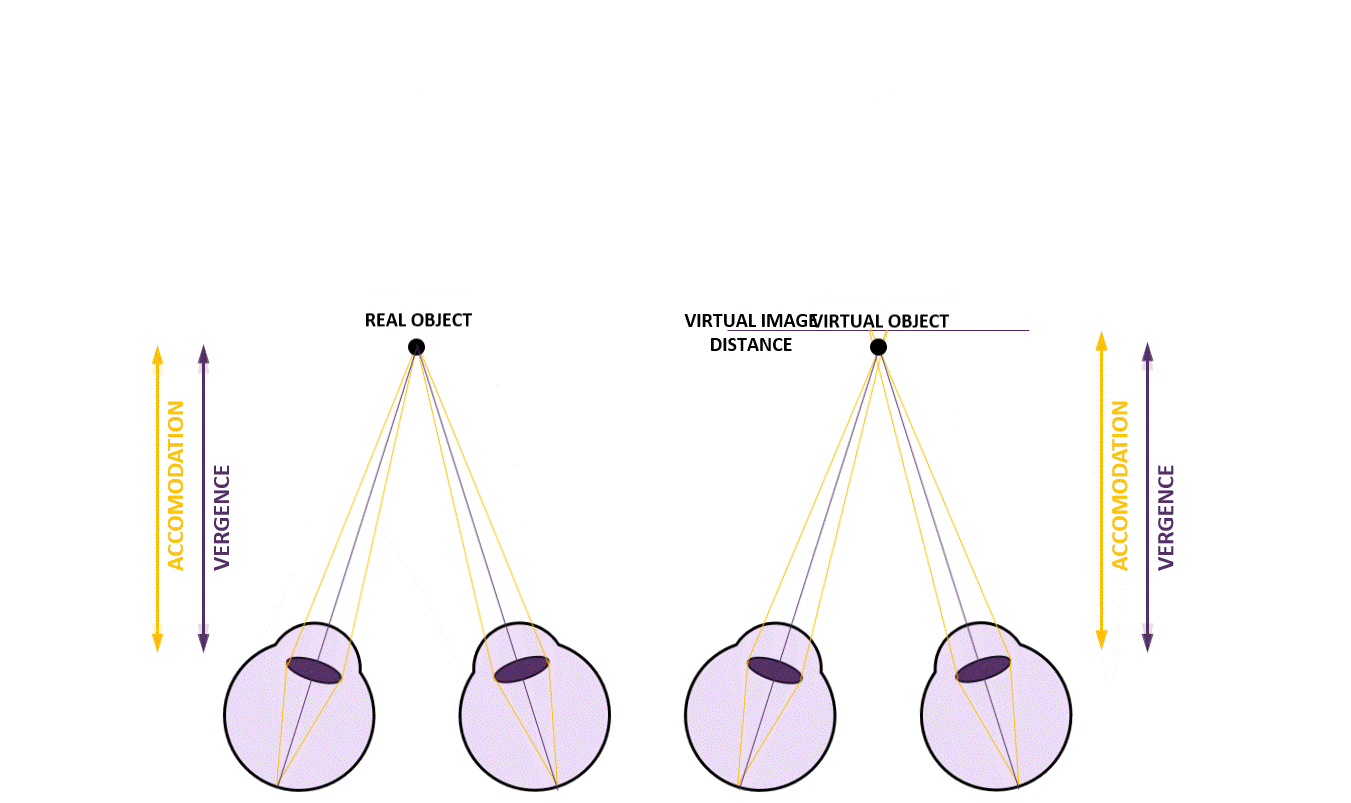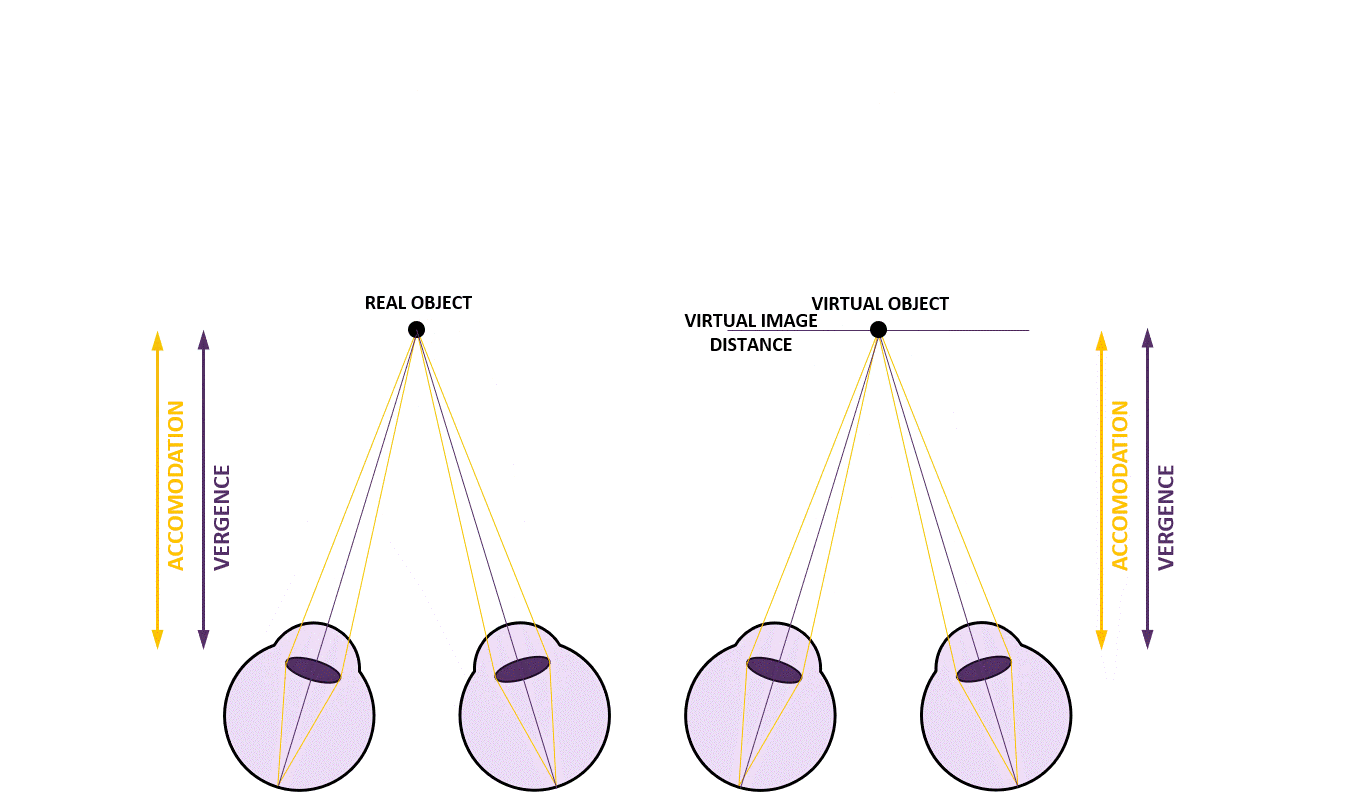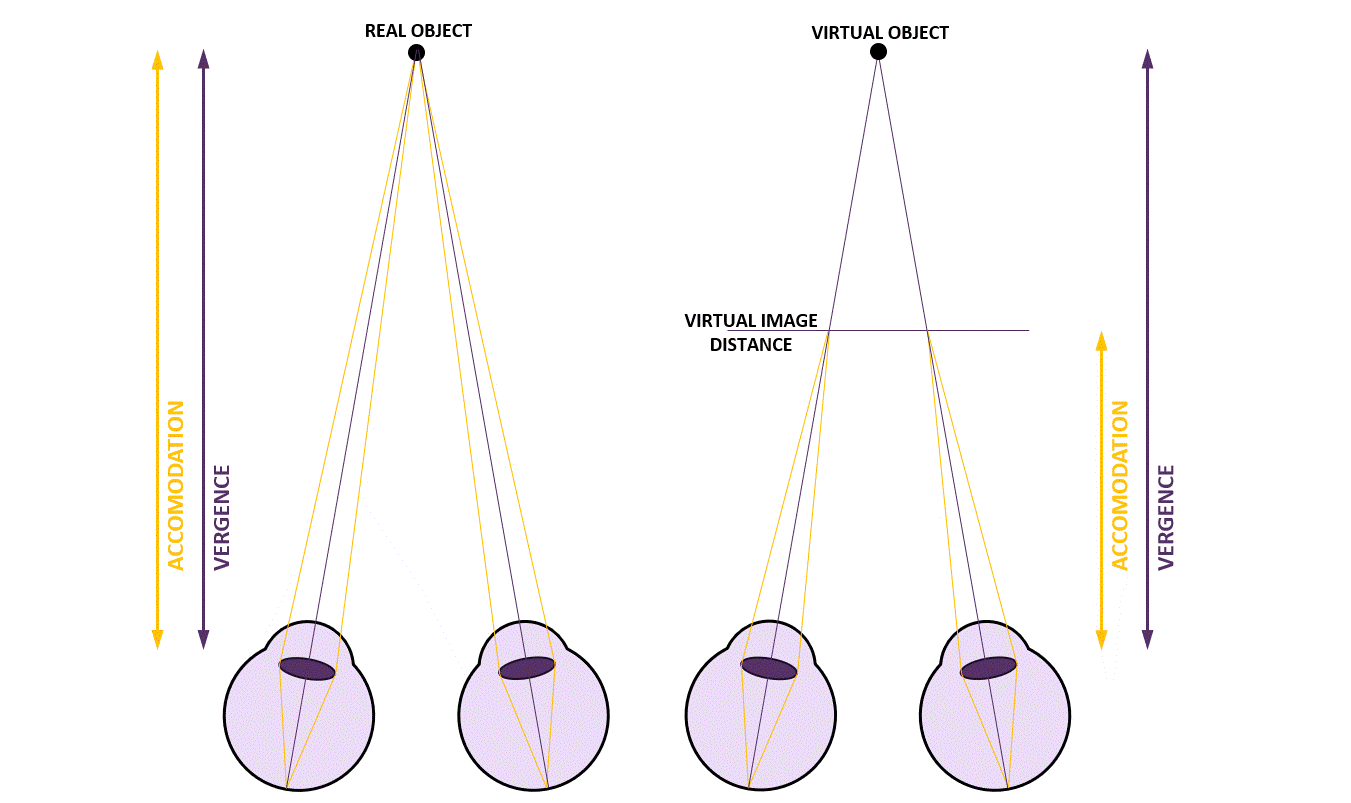 Figure 1: Mismatch between viewing a virtual object close up.
Figure 1: Mismatch between viewing a virtual object close up.
This limitation restricts how virtual content can be presented, particularly for objects close to the user, limiting the design possibilities and immersion of XR experiences.
Dynamic focal adjustment
Dynamic focal adjustment, also known as varifocal display technology, offers a solution to align the focal distance of XR displays with the perceived depth of virtual objects. By adjusting the focal plane in real-time, this technology harmonises vergence and accommodation cues, reducing discomfort and enabling a more natural viewing experience.
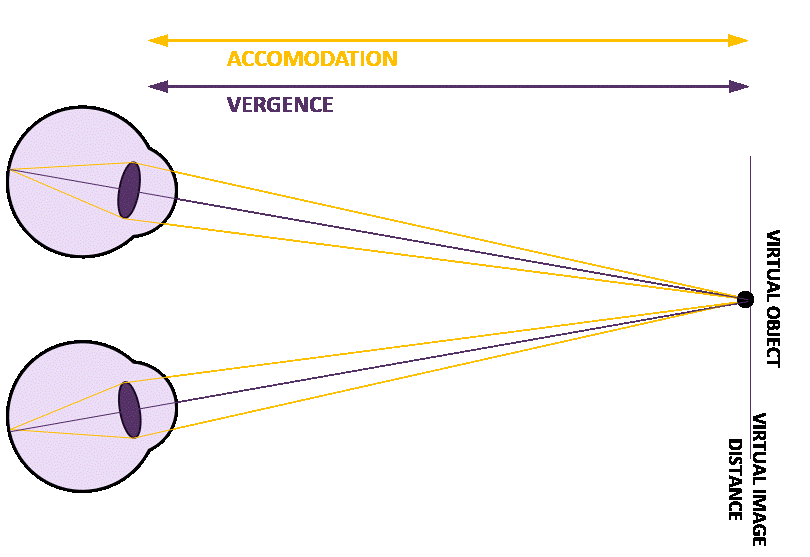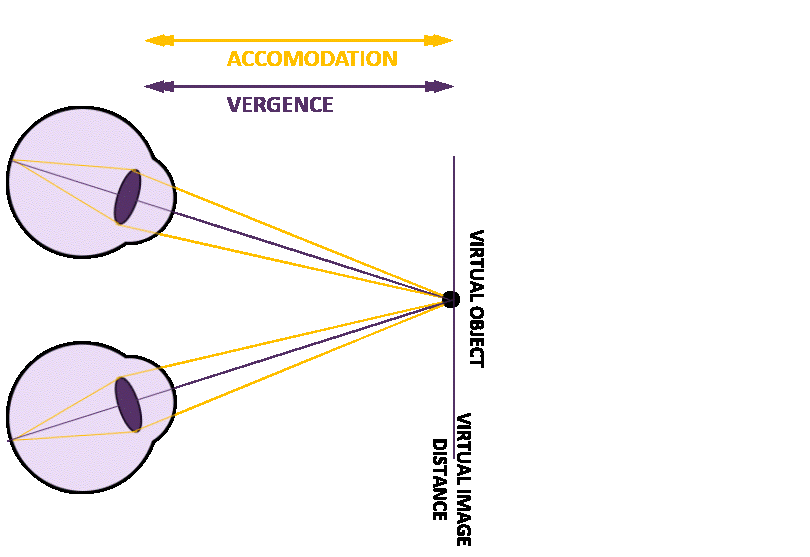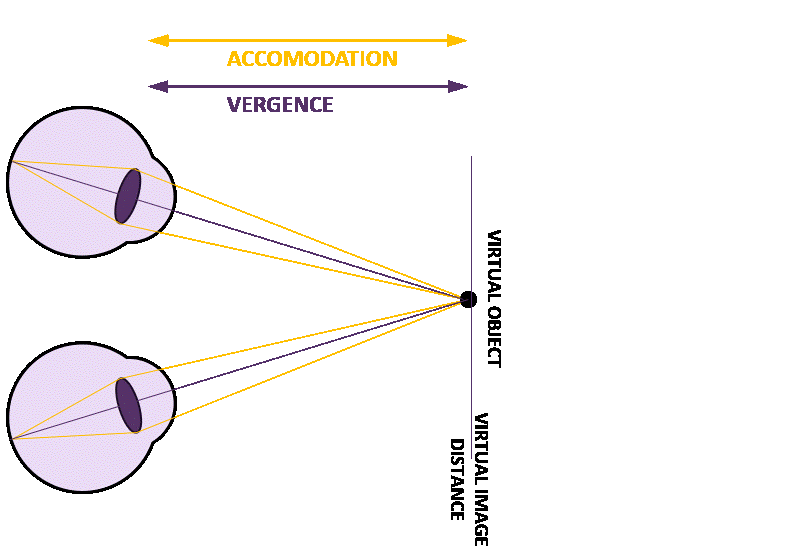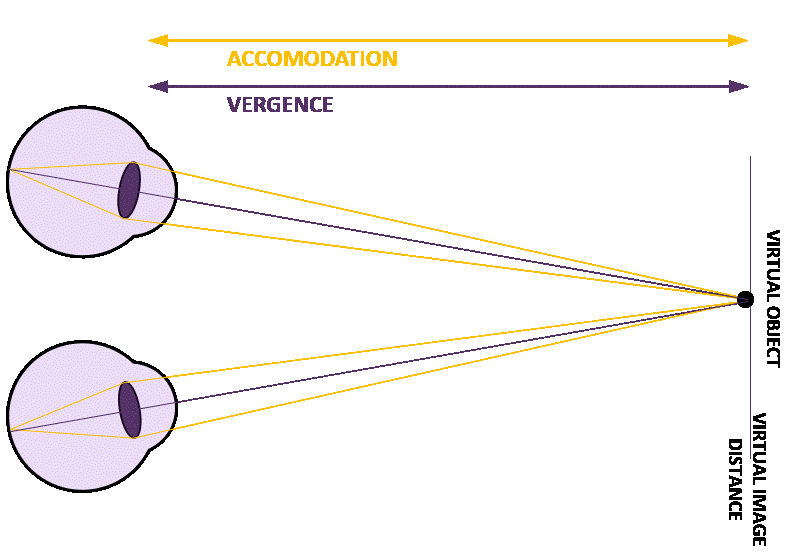 Figure 2: Concept of dynamic focal adjustment to address VAC
Figure 2: Concept of dynamic focal adjustment to address VAC
However, implementing this solution in XR devices faces several challenges:
- Miniaturisation: Actuation mechanisms must be powerful enough to move the display or other optical components while being small enough to fit within the compact form factor of head-mounted devices (HMDs).
- Lightweight: Additional components cannot compromise user comfort by adding weight.
- Low power consumption: Devices must operate efficiently to avoid additional heat generation and maximise usage time in battery-powered devices.
SMA: The actuator solution for XR
CML’s SMA actuators are uniquely suited to overcome these challenges, making them an ideal choice for dynamic focal adjustment and other applications in XR devices.
Compact, lightweight design
SMA actuators use SMA wires thinner than a human hair to create motion, so they can be made incredibly small and light. This compactness allows actuators to be integrated into the limited space around or under XR displays without disrupting the device's design or ergonomics. Their small footprint ensures that XR headsets remain lightweight and wearable, even with added functionality.
Energy efficiency with Zero Hold Power
CML has developed a Zero Hold Power (ZHP) feature, enabling SMA actuators to use power only when changing the lens position, not while maintaining it. This drastically reduces energy consumption, an essential feature for portable, battery-powered headsets.
High force-to-mass ratio
SMA wires produce a high force relative to their size and mass, making them capable of moving substantial payloads, such as displays or other optical components. By using geared designs, CML’s SMA actuators can achieve the required strokes ranging from hundreds of microns to several mm, depending on the headset design.
Precision and responsiveness
SMA actuators offer submicron precision, ensuring that adjustments to the lens position are both accurate and responsive. This precision is crucial for maintaining visual clarity and delivering a seamless user experience in dynamic virtual environments.
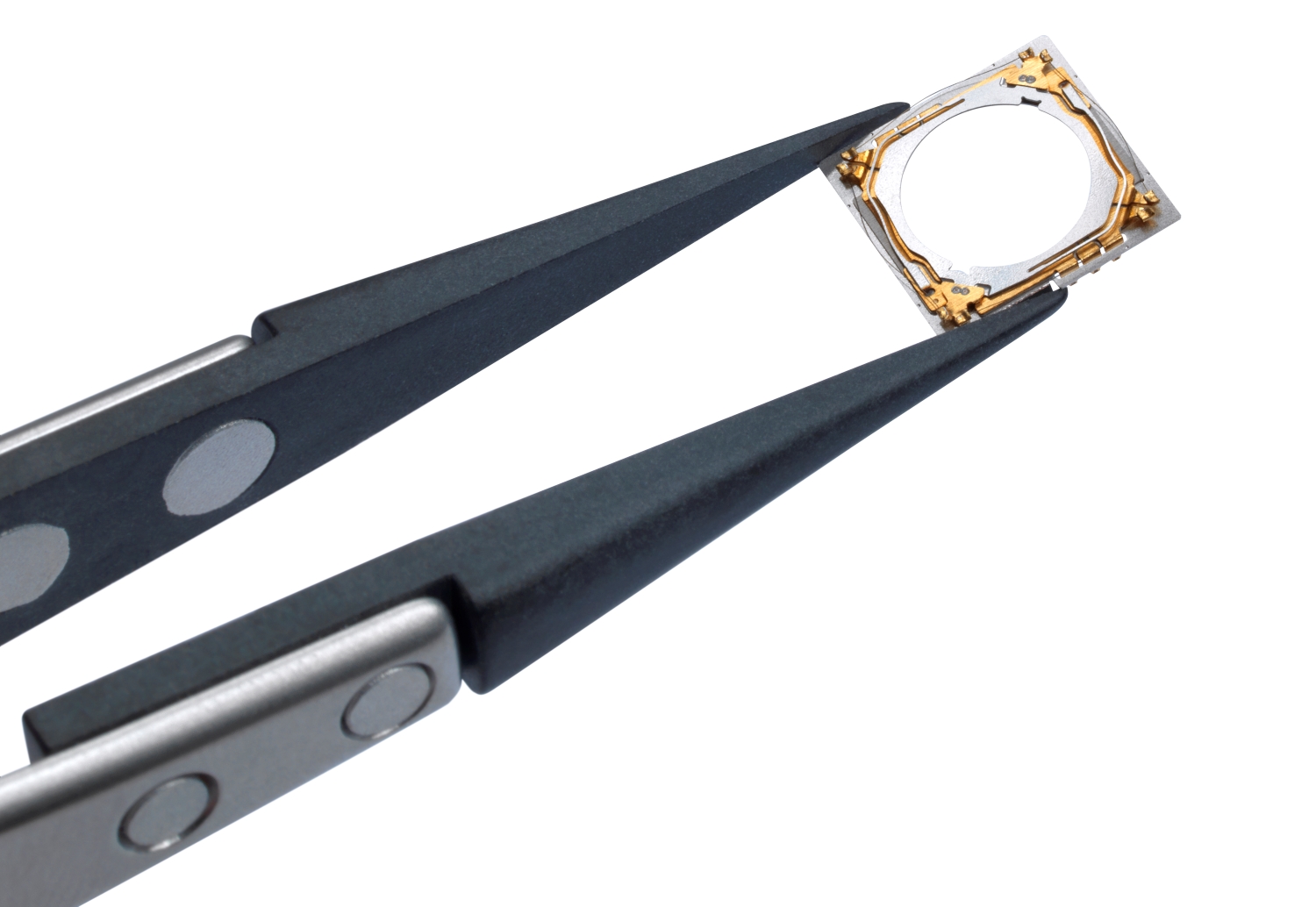 Figure 3: Photo of an SMA optical image stabilisation (OIS) actuator for smartphone cameras. CML's compact, high force SMA actuator technology has shipped in over 80m smartphones to date.
Figure 3: Photo of an SMA optical image stabilisation (OIS) actuator for smartphone cameras. CML's compact, high force SMA actuator technology has shipped in over 80m smartphones to date.
The Future of XR with SMA technology
CML’s SMA technology is being developed to provide a range of innovative solutions to the challenges facing AR/VR/XR. By addressing the VAC challenge, SMA actuators can help XR devices deliver a better level of immersion and comfort. Their compact design, energy efficiency, and high precision can enable varifocal displays to potentially become a standard feature in future XR headsets, improving the way users experience virtual and augmented realities.
CML is proud to be a part of this exciting space and to contribute to the creation of devices that enhance user experiences across industries.
About Cambridge Mechatronics Ltd: CML is a global leader in the development of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) technology for precision actuation. From enabling dynamic focal adjustment in XR to enhancing smartphone cameras, CML’s SMA actuators deliver high-force, low-power, and compact solutions for a wide range of applications. To learn more, get in touch.
